I. Introduction to Gym Workouts for Beginner Females
A. Understanding the Importance of Exercise for Women
Exercise plays a vital role in women’s overall health and well-being. Regular physical activity not only helps in weight management but also reduces the risk of chronic diseases such as heart disease, diabetes, and osteoporosis. Additionally, exercise has been shown to improve mental health, boost energy levels, and enhance confidence and self-esteem.

B. Common Misconceptions about Gym Workouts for Females
There are several misconceptions surrounding gym workouts for women. One common myth is that lifting weights will make females bulk up. However, this is far from the truth. Women have lower testosterone levels compared to men, which makes it difficult for them to build significant muscle mass naturally. Instead, weightlifting helps women develop lean muscles, improve bone density, and increase metabolism.
C. Benefits of Gym Workouts for Beginner Females
Engaging in gym workouts offers numerous benefits for beginner females. Firstly, it aids in burning fat and toning the body. Regular exercise helps boost the metabolism, allowing the body to burn calories more efficiently. As a result, women can achieve their weight loss goals and develop a toned physique. Additionally, gym workouts improve cardiovascular health, increase stamina, enhance flexibility, and strengthen muscles, bones, and joints.
II. Getting Started: Essential Preparations for Gym Workouts
A. Setting Goals and Tracking Progress
Before starting any gym routine, it is crucial for beginner females to set realistic goals. Whether it’s weight loss, strength building, or overall fitness improvement, clearly defining these goals helps stay motivated and on track. Additionally, tracking progress through measurements, photos, or keeping a workout journal allows individuals to monitor their achievements and make necessary adjustments along the way.
B. Choosing the Right Gym and Trainer
Selecting the right gym is essential for a positive workout experience. Look for facilities that provide a welcoming and inclusive environment that focuses on the needs of women. It’s also beneficial to seek guidance from qualified trainers experienced in working with beginner females. A knowledgeable trainer can create a personalized workout plan, teach proper form and technique, and provide motivation and support throughout the fitness journey.
C. Important Safety Considerations
Safety should always be a top priority when starting a gym workout routine. Beginners should consult with their healthcare provider before beginning any new exercise program. It’s crucial to listen to the body, start slowly, and gradually increase the intensity and duration of workouts. Using proper equipment, maintaining proper form, and warming up and cooling down adequately are also essential to prevent injuries

III. Full-Body Workout Routine for Weight Loss and Toning
A. Warm-up Exercises to Prep the Body
Cardio Warm-up
Before diving into strength training, it’s important to warm up the body with a few minutes of cardio. This could include activities such as jogging, cycling, or jumping rope, which increase heart rate and blood flow, thus preparing the muscles for the upcoming workout.

- Dynamic Stretching
Dynamic stretching involves active movements that mimic the exercises to be performed. It helps improve flexibility and range of motion by gradually increasing the body’s temperature and muscle elasticity. Dynamic stretches can include arm circles, leg swings, or walking lunges.

- Activation Exercises
Activation exercises focus on activating specific muscles before engaging in compound movements. These exercises help improve mind-muscle connection and enhance overall performance. Examples of activation exercises include glute bridges, bird dogs, and band walks.
B. Strength Training Exercises for Fat Burning and Toning
Squats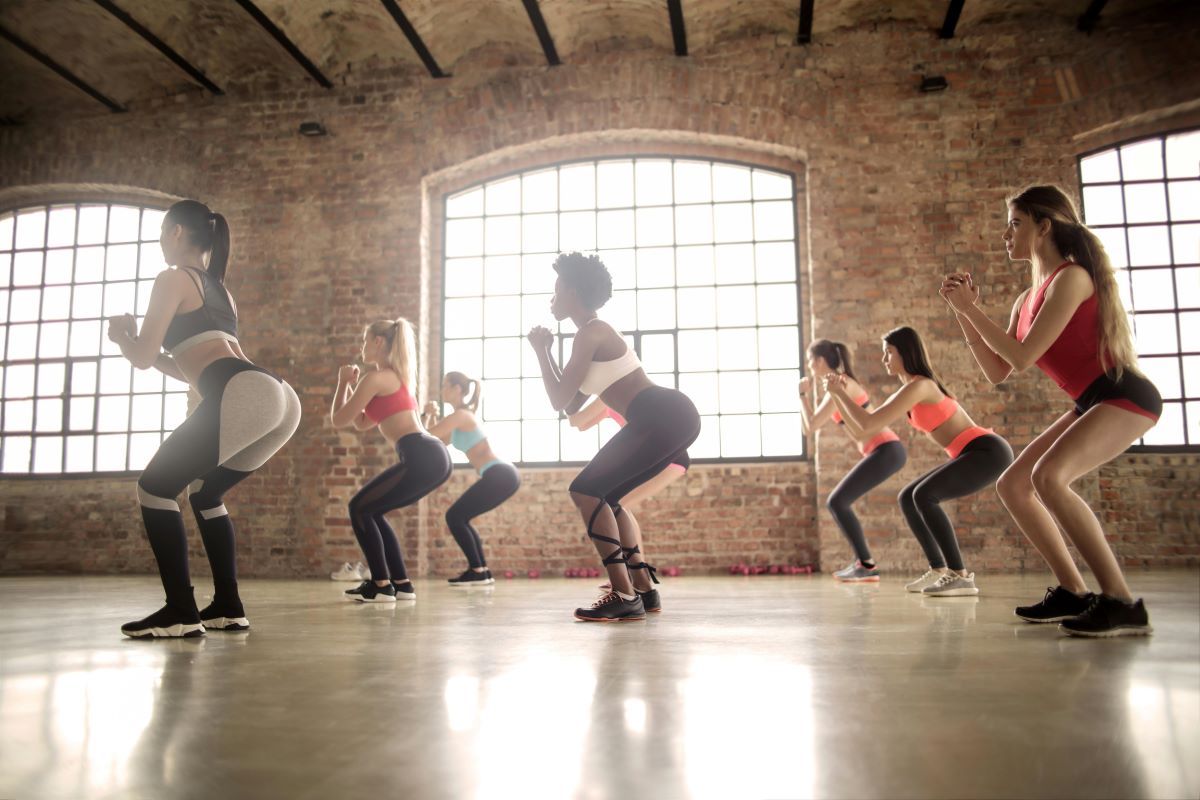
Squats are a compound exercise that targets multiple muscle groups, including the quads, hamstrings, glutes, and core. Proper form is crucial while performing squats to prevent any strain or injury. Starting with bodyweight squats and gradually progressing to weighted squats can effectively build strength, burn calories, and tone the lower body.
How to do:
- Starting Position: Stand upright with feet shoulder-width apart, knees slightly bent, and knees not extending beyond the toes.
- Lower the Body: Lower your body by bending the knees and pushing the hips back, keeping the weight primarily on the heels.
- Knee and Foot Alignment: Ensure that the knees do not go beyond the toes and do not collapse inward or outward. This helps maintain even stress on the quadriceps and ensures safety.
- Lift the Body: Use the quadriceps and glutes to push the body back up to the starting position.
- Repeat: Perform 3 sets of 8-12 repetitions each, depending on your fitness level and personal strength.
Lunges
Lunges are another powerful lower body exercise that engages the glutes, hamstrings, quads, and calves. They can be performed in various ways, such as forward lunges, reverse lunges, or walking lunges. Adding dumbbells or kettlebells can further challenge the muscles and promote strength development.
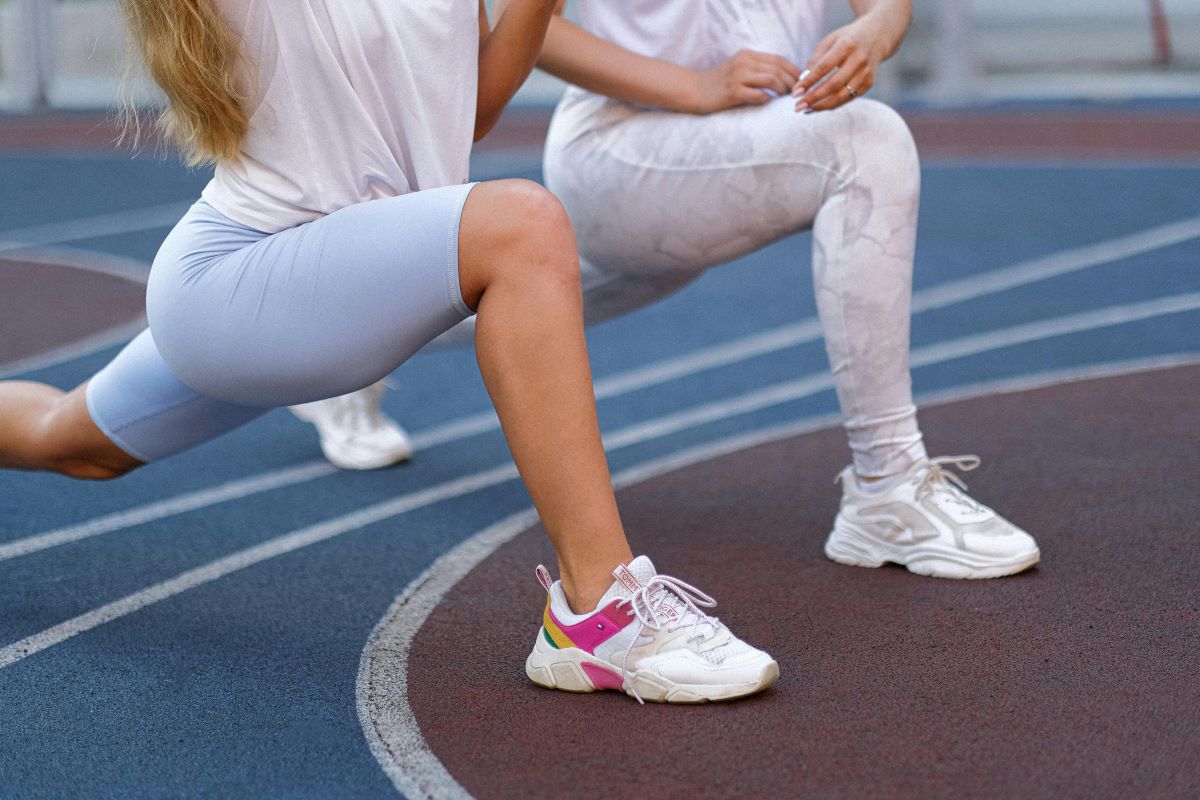

How to do:
- Starting Position: Stand with feet hip-width apart, maintaining an upright posture.
- Step Forward or Backward: Take a step forward or backward with one foot, lowering the body until both knees form 90-degree angles.
- Maintain Proper Alignment: Ensure the front knee is directly above the ankle, and the back knee hovers slightly above the ground. Keep the torso straight and avoid leaning too far forward.
- Push Back to Starting Position: Use the front foot to push back to the starting position, bringing both feet together.
- Repeat on Both Legs: Perform the lunges on both legs, alternating between them.
- Add Resistance for Intensity: To intensify the workout, hold dumbbells or kettlebells in each hand while performing lunges.
- Sets and Repetitions: Aim for 3 sets of 10-15 repetitions per leg, adjusting the intensity based on your fitness level.
Lunges not only contribute to lower body strength but also enhance stability and balance, making them a valuable addition to any comprehensive fitness routine.
Push-ups:
Push-ups target the chest, triceps, shoulders, and core muscles. They can be modified to suit individual fitness levels, such as performing push-ups on knees or against a wall. Gradually increasing the number of repetitions and improving form can enhance overall upper body strength and muscle tone.
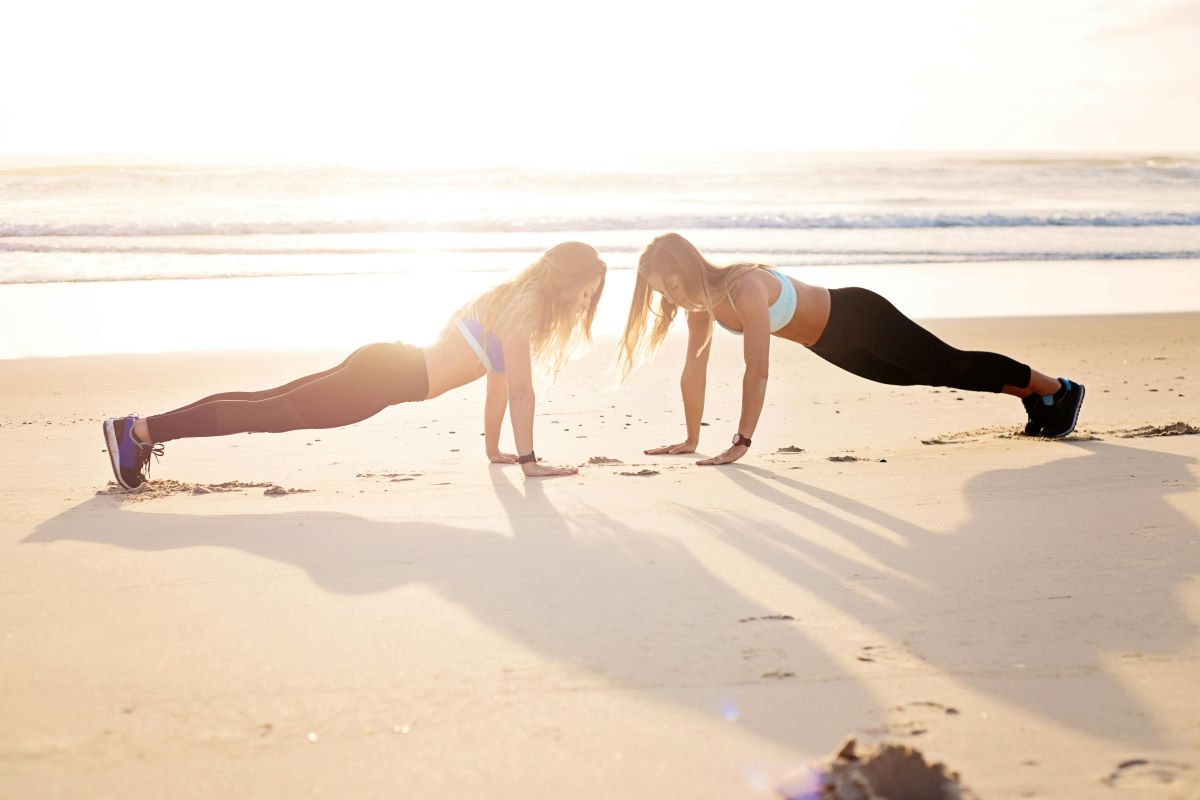

How to do:
Starting Position: Begin in a plank position with hands placed slightly wider than shoulder-width apart, and the body forming a straight line from head to heels.
Lower the Body: Lower the chest towards the ground by bending the elbows, keeping them close to the body. Maintain a straight line from head to heels.
Maintain Core Engagement: Keep the core engaged throughout the movement to ensure stability and prevent overarching or sagging of the lower back.
Push Back Up: Push through the palms to return to the starting position, fully extending the arms.
Modification Options:
- Knee Push-ups: Perform the push-up position with knees on the ground.
- Wall Push-ups: Stand facing a wall and perform the push-up motion against the wall.
Repetition and Progression: Start with a manageable number of repetitions and gradually increase as strength improves. Focus on maintaining proper form.
Sets and Repetitions: Aim for 3 sets of 10-15 repetitions, adjusting based on individual fitness levels.
Push-ups offer a comprehensive upper body workout, contributing to increased strength, muscle endurance, and overall functional fitness.
C. High-Intensity Interval Training (HIIT) for Maximizing Results
- Introduction to HIIT
High-Intensity Interval Training (HIIT) involves alternating intense bursts of exercise with brief rest periods. This form of training is highly effective for fat loss, increasing cardiovascular fitness, and boosting metabolism. HIIT workouts can include exercises such as burpees, mountain climbers, or high knees.
- HIIT Exercises
There are several HIIT exercises suitable for beginner females. Examples include squat jumps, plank jacks, jumping lunges, or bicycle crunches. These exercises elevate heart rate, challenge the muscles, and promote calorie burning even after the workout.
- Cool-down and Stretching
After completing the workout, it’s important to cool down the body gradually. This can be achieved through light cardio exercises such as walking and followed by static stretching. Stretching helps improve flexibility, reduce muscle soreness, and prevent injury.
IV. Targeted Workout Routine for Building Strength and Muscle
A. Introduction to Strength Training
- Benefits of Strength Training for Women
Strength training offers numerous benefits for women. It helps increase lean muscle mass, which in turn boosts metabolism and aids in weight management. Additionally, strength training improves bone density, reduces the risk of osteoporosis, enhances joint stability, and promotes overall functional strength.
- Dispelling Myths about Women and Weightlifting
There is a common myth that weightlifting will make women bulky or masculine. However, due to lower testosterone levels compared to men, females do not have the same capacity to develop significant muscle mass naturally. Instead, strength training helps women achieve a toned and sculpted physique while reaping the many health benefits associated with resistance training.
- Understanding Repetitions, Sets, and Rest Periods
In strength training, repetitions (reps) refer to the number of times an exercise is performed consecutively, while sets indicate the number of times those repetitions are completed. Rest periods between sets allow the muscles to recover and should be adjusted based on individual goals and fitness level.
B. Compound Exercises for Full-Body Strength
- Deadlifts
Deadlifts are a compound exercise that targets the posterior chain, including the glutes, hamstrings, lower back, and core. Proper form and technique are crucial to prevent injuries. Starting with lighter weights and gradually increasing the load can help develop overall strength and improve posture. Executing proper form and technique is imperative to prevent injuries and maximize the benefits of this powerful movement.
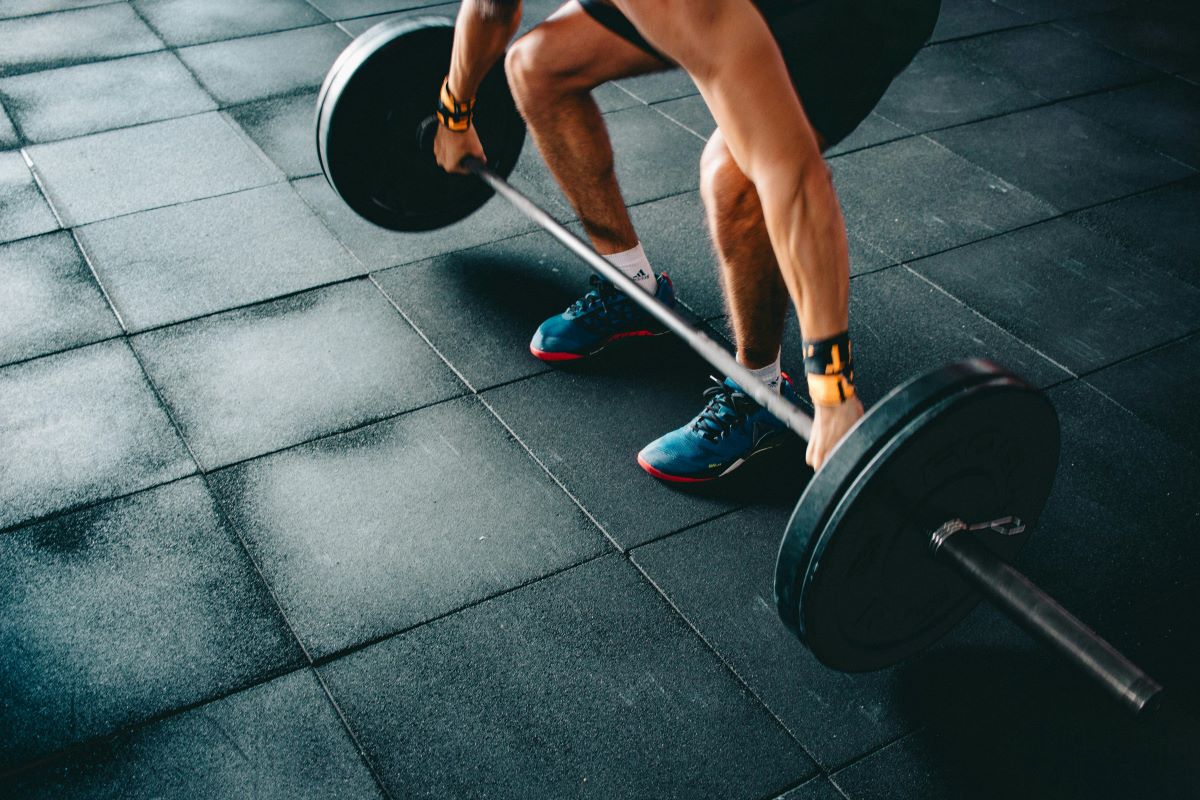

How to do:
Starting Position: Stand with feet hip-width apart, toes pointing forward. The barbell should be placed in front of you, aligned with the mid-foot.
Grip the Barbell: Bend at the hips and knees to lower your body, grasping the barbell with an overhand grip (palms facing you) or mixed grip (one palm facing you, one facing away).
Set Your Back: Ensure your back is straight, chest lifted, and shoulders pulled back. Engage your core to maintain stability.
Lift the Barbell: Push through your heels, extend your hips and knees simultaneously, lifting the barbell as you stand upright. Keep the barbell close to your body throughout the movement.
Full Extension: Stand tall with your hips and knees fully extended, shoulders back, and chest lifted at the top of the movement.
Lower the Barbell: Hinge at the hips and bend your knees to lower the barbell back to the ground, maintaining control and proper form.
Repetition and Progression: Start with a moderate weight and aim for 3 sets of 8-12 repetitions. Gradually increase the weight as your strength improves.
Deadlifts not only build strength but also contribute to improved posture, enhanced stability, and overall functional fitness. Ensure proper form and consider seeking guidance from a fitness professional, especially if you are new to this exercise.
- Bench Press
The bench press focuses on the chest, shoulders, and triceps, making it an effective upper body compound exercise. Beginners can start with lighter weights or even use resistance bands to develop strength gradually. Proper form, including maintaining a stable grip and engaging the core, is essential for optimal results.
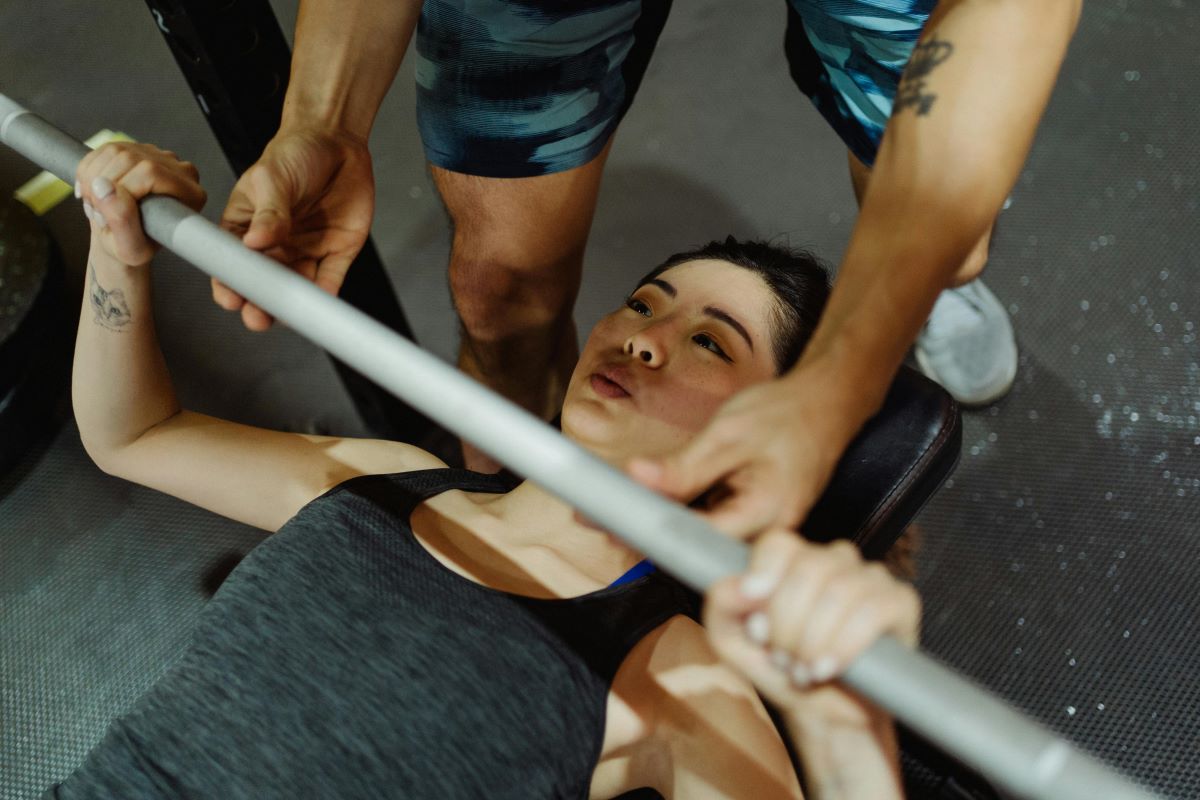
How to do:
Starting Position: Lie on a flat bench with your feet flat on the ground. Position the barbell over your chest, hands slightly wider than shoulder-width apart.
Grip the Barbell: Grasp the bar with an overhand grip, keeping your wrists straight. Ensure a secure grip on the barbell.
Lower the Barbell: Lower the barbell to your chest by bending your elbows. The bar should touch your chest lightly, and your elbows should form a 90-degree angle.
Push the Barbell Up: Push the barbell back up to the starting position, fully extending your arms. Keep your back, head, and buttocks firmly on the bench.
Controlled Movement: Perform the exercise in a controlled manner, avoiding rapid movements or bouncing the barbell off the chest.
Engage the Core: Keep your core engaged throughout the movement to provide stability and protect your lower back.
Breathing: Inhale as you lower the barbell and exhale as you push it back up.
Repetition and Progression: Start with a manageable weight, aiming for 3 sets of 8-12 repetitions. Gradually increase the weight as your strength improves.
The bench press is a foundational exercise in strength training, promoting upper body development and muscle growth. Consistent practice with proper form is key to reaping the full benefits of this classic compound movement.
- Pull-ups
Although challenging, pull-ups are a highly effective exercise for building upper body strength. They primarily work the muscles in the back, biceps, and shoulders. Beginners can start with assisted pull-ups or use resistance bands to gradually develop the necessary strength to perform unassisted pull-ups.
How to do:
Grip the Bar: Stand beneath a pull-up bar, palms facing away from you, and grip the bar slightly wider than shoulder-width apart.
Hang Position: Hang from the bar with your arms fully extended, ensuring your body is straight and your feet are off the ground.
Pull Your Body Up: Initiate the pull-up by engaging your back muscles. Pull your chest towards the bar, keeping your elbows close to your body.
Chin Above the Bar: Continue pulling until your chin is above the bar. Focus on using your back muscles rather than relying solely on your arms.
Lower Your Body: Lower your body in a controlled manner, fully extending your arms. Avoid swinging or using momentum.
Controlled Breathing: Inhale as you lower your body, and exhale as you pull yourself up.
Modification Options: For beginners, consider using an assisted pull-up machine, resistance bands, or performing negative pull-ups (lowering yourself down slowly).
Repetition and Progression: Aim for 3 sets of 5-10 repetitions, adjusting the difficulty as needed. Gradually increase the number of repetitions as your strength improves.
Pull-ups are an excellent measure of upper body strength and can be a challenging but rewarding addition to any fitness routine. Consistency and progression are key to mastering this fundamental bodyweight exercise.
C. Isolation Exercises for Specific Muscle Groups
- Bicep Curls
Bicep curls target the muscles in the front of the upper arm. Using dumbbells or a barbell, beginners can perform bicep curls in a controlled manner, focusing on contracting the biceps while maintaining proper form. Gradually increasing the weight can help individuals build strength and improve muscle definition.
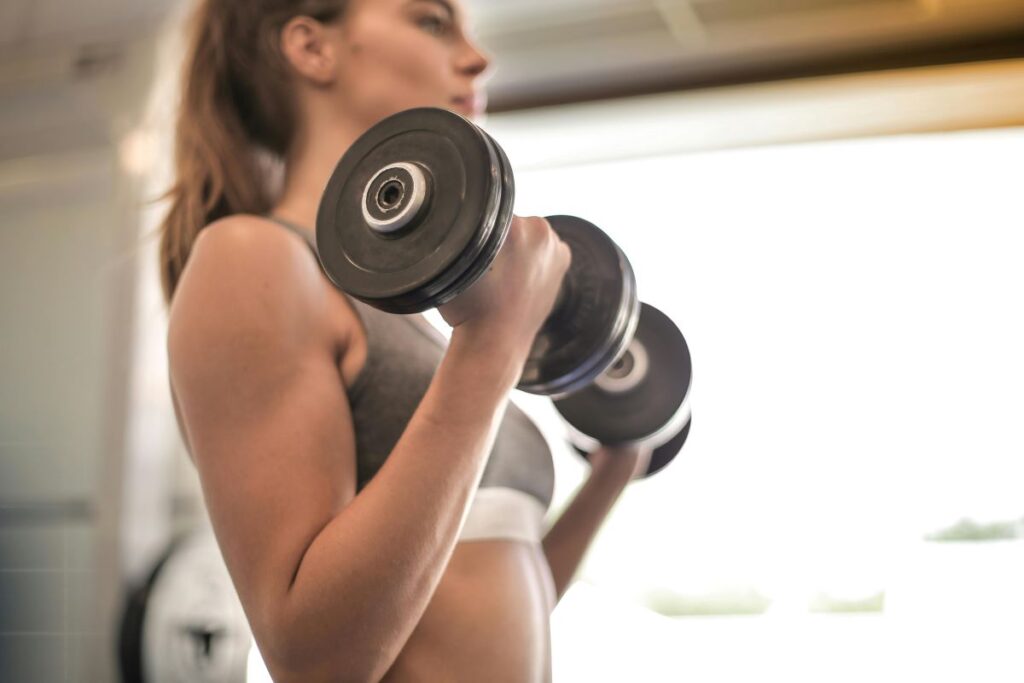

How to Perform:
Starting Position: Stand with your feet shoulder-width apart, holding a dumbbell in each hand or gripping a barbell with an underhand grip.
Grip and Posture: Keep a neutral spine, engage your core, and ensure your elbows are close to your torso. Palms should be facing forward.
Curl the Weights: In a controlled motion, lift the weights towards your shoulders by flexing at the elbow. Keep your upper arms stationary.
Full Contraction: Squeeze your biceps at the top of the movement, ensuring a full contraction of the muscle.
Lower the Weights: Slowly lower the weights back to the starting position, resisting the pull of gravity.
Controlled Breathing: Inhale as you lower the weights and exhale as you lift them.
Repetition and Sets: Aim for 3 sets of 10-15 repetitions, selecting a weight that challenges your muscles but allows you to maintain proper form.
Progressive Overload: Gradually increase the weight as your strength improves to continue challenging your biceps.
Bicep curls are an effective way to isolate and strengthen the biceps, contributing to arm development and overall upper body aesthetics. Consistency, proper form, and gradual progression are key factors in achieving optimal results with this exercise.
- Tricep Dips
Tricep dips primarily engage the triceps, along with the chest and shoulders. They can be performed using a bench, chair, or dip bars. Beginners can start with assisted tricep dips or perform modified versions until they build sufficient strength to execute full dips.
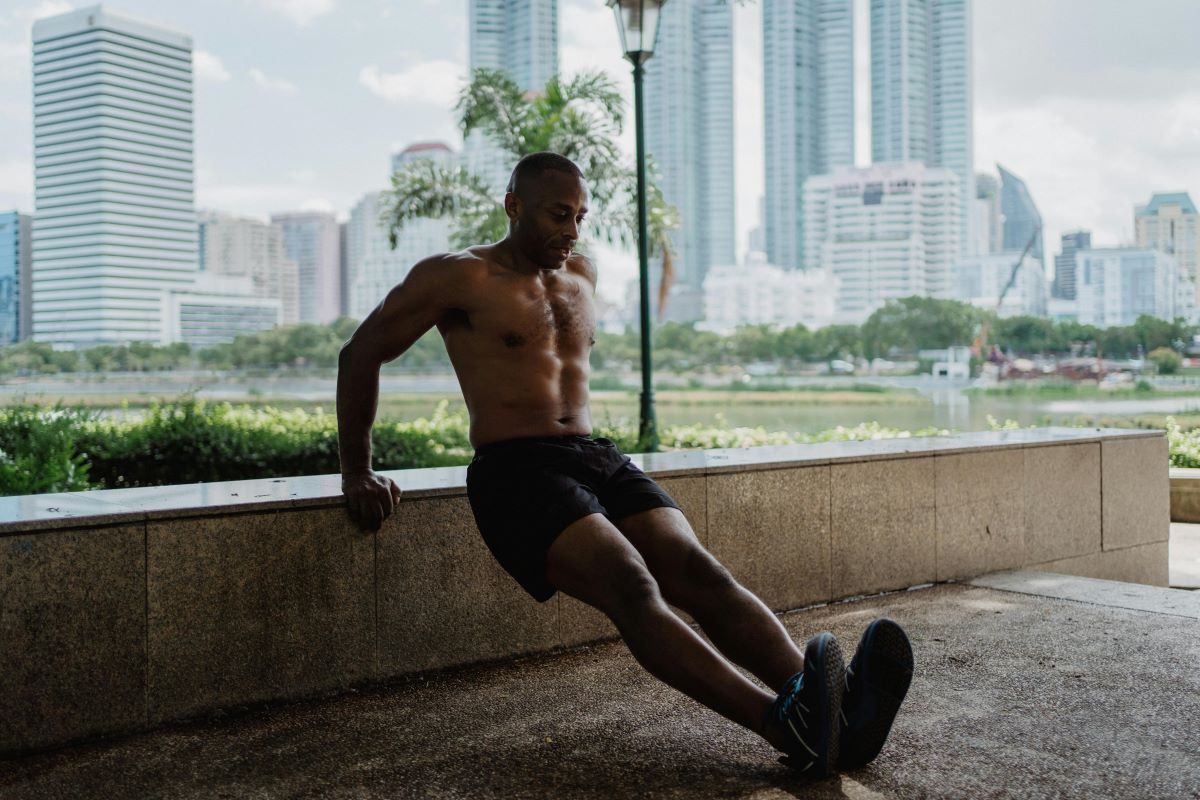

How to do:
Using Parallel Bars or Bench: Position yourself between parallel bars or facing away from a bench or chair. Place your hands on the bars or the edge of the bench, shoulder-width apart.
Starting Position: Extend your legs out in front of you, keeping your heels on the ground. Maintain a slight forward lean with your torso.
Lower Your Body: Bend your elbows to lower your body, keeping your back close to the bars or bench. Lower until your elbows are at a 90-degree angle.
Push Back Up: Push through your palms to straighten your arms and return to the starting position, fully extending your elbows.
Controlled Breathing: Inhale as you lower your body and exhale as you push back up.
Using a Bench or Chair: Sit on the edge of the bench or chair with your hands gripping the edge. Move your hips forward and lower your body, then push back up.
Assisted Tricep Dips: For beginners, use a resistance band or have a partner assist you by holding your legs, making the movement more manageable.
Repetition and Sets: Aim for 3 sets of 10-15 repetitions, adjusting the difficulty as needed. Increase the challenge as your tricep strength improves.
Tricep dips provide an effective way to target and strengthen the triceps, contributing to improved arm definition and overall upper body strength. Consistency and proper form are key to mastering this exercise.
- Leg Press
The leg press machine targets the muscles in the lower body, including the quadriceps, hamstrings, and glutes. Adjusting the weight according to individual abilities, beginners can gradually increase resistance to build lower body strength and muscle tone.
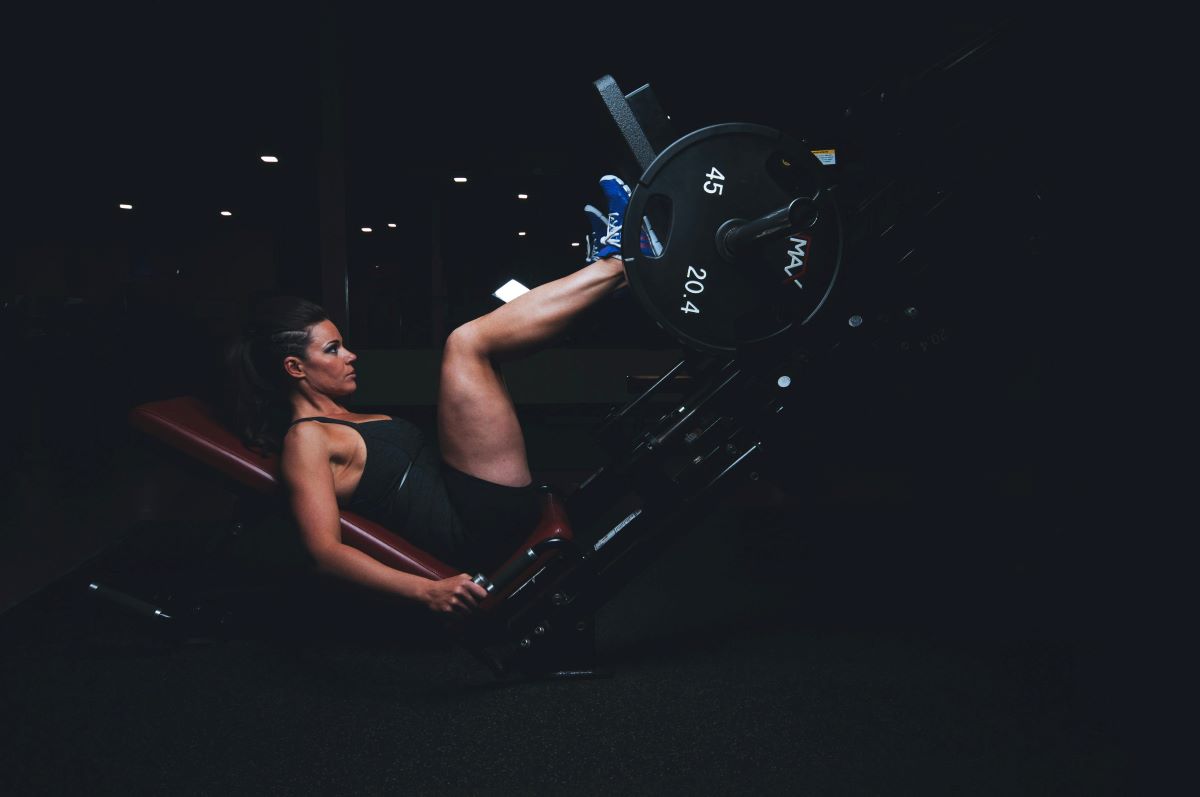

How to Perform:
Machine Setup: Sit on the leg press machine with your back flat against the backrest. Place your feet on the footplate about shoulder-width apart.
Adjust Seat Position: Ensure the seat is set at a comfortable position, allowing your knees to form a 90-degree angle when you lower the weight.
Grip Handles: Grasp the handles on the sides of the machine to maintain stability throughout the exercise.
Push the Platform: Press through your heels to extend your legs and push the platform away from you. Fully extend your legs without locking your knees.
Controlled Movement: Lower the platform back towards your body in a controlled manner, allowing your knees to bend to approximately a 90-degree angle.
Breathing: Inhale as you lower the platform, and exhale as you push it away.
Foot Placement: Experiment with different foot placements to target specific areas of the legs. A higher foot placement may emphasize the glutes, while a lower foot placement may engage the quadriceps more.
Repetition and Sets: Aim for 3 sets of 10-15 repetitions, adjusting the weight to match your fitness level. Gradually increase resistance as your lower body strength improves.
The leg press machine offers a safe and effective way to strengthen the muscles in the lower body. Consistent practice, proper form, and a progressive approach to resistance contribute to the development of lower body strength and muscle tone.
V. Incorporating Cardiovascular Exercises into Your Routine
A. Importance of Cardiovascular Exercise for Women
Cardiovascular exercises provide numerous benefits for women’s overall health and fitness. They help improve heart health, increase lung capacity, lower blood pressure, and reduce the risk of chronic diseases. Additionally, cardiovascular activities aid in weight management, boost mood and mental well-being, and enhance endurance and stamina.
B. Different Types of Cardiovascular Exercises
- Running
Running is a popular and accessible cardiovascular exercise that can be performed both outdoors and on a treadmill. It effectively increases heart rate, burns calories, and strengthens lower body muscles. Beginners can start with a combination of walking and jogging and gradually progress to continuous running.
- Cycling
Cycling is a low-impact cardiovascular exercise that offers both outdoor and indoor options. It is gentle on the joints and helps develop lower body strength. Whether using a stationary bike or riding outdoors, beginners can adjust intensity and duration according to their fitness level.
- Swimming
Swimming is a full-body cardiovascular exercise that is gentle on the joints and offers resistance training benefits. It engages multiple muscle groups while providing a low-impact workout. Beginners can start with basic strokes and gradually increase the intensity by incorporating intervals or advanced strokes.
C. Creating a Cardiovascular Workout Plan
- Interval Training
Interval training involves alternating between periods of high-intensity exercise and active recovery. It can be applied to various cardiovascular exercises such as running, cycling, or swimming. Interval training promotes calorie burning, boosts endurance, and keeps the workout challenging and engaging.
- Steady-State Cardio
Steady-state cardio refers to maintaining a consistent intensity throughout the duration of the exercise. This type of training is beneficial for building endurance and improving cardiovascular health. Activities like jogging, brisk walking, or cycling can be performed steadily for a prolonged period.
- Cross-Training
Cross-training involves incorporating different cardiovascular exercises into a workout routine to prevent boredom and promote overall fitness. It allows individuals to engage different muscle groups, prevent overuse injuries, and enhance overall performance. Mixing activities like running, cycling, and swimming provides variety and keeps the workouts enjoyable.
VI. Essential Nutrition Tips for Female Gym Goers
A. Importance of Proper Nutrition for Fitness Goals
Proper nutrition plays a crucial role in achieving fitness goals. It provides the necessary fuel for workouts, aids in muscle recovery and growth, and supports overall health. Balancing macronutrients, consuming adequate calories, and staying hydrated are key components for optimal performance and results.
B. Macronutrient Basics: Proteins, Carbohydrates, and Fats
Proteins, carbohydrates, and fats are the three macronutrients that form the foundation of a balanced diet.
- Proteins are essential for muscle repair and growth. Sources of protein include lean meats, poultry, fish, dairy products, legumes, and plant-based proteins like tofu and tempeh.
- Carbohydrates are the primary energy source for the body. Incorporating complex carbohydrates such as whole grains, fruits, and vegetables provides sustained energy throughout workouts.
- Fats are important for hormone production and healthy brain function. Choosing healthy fat sources like avocados, nuts, seeds, and fatty fish helps maintain overall health.
C. Nutrition Strategies for Fat Loss and Muscle Gain
- Balanced Meal Planning
Designing balanced meals involves incorporating all three macronutrients along with a variety of fruits, vegetables, and whole foods. Planning meals ahead of time can help maintain consistency in nutrient intake and support fitness goals.
- Tracking Caloric Intake
Tracking caloric intake can provide valuable insights into energy balance. Apps or food journals can help monitor portion sizes, track macronutrient ratios, and ensure a reasonable caloric deficit or surplus based on individual goals.
- Hydration and Recovery
Staying hydrated is vital for optimal performance and recovery. Drinking water before, during, and after workouts helps replace lost fluids and maintain electrolyte balance. Additionally, ensuring adequate rest and recovery is essential for muscle repair, injury prevention, and overall well-being.
Summary
Recap of the Benefits of Gym Workouts for Beginner Females
Gym workouts offer a multitude of benefits for beginner females. They help burn fat, build strength, improve cardiovascular health, and enhance overall well-being. Incorporating a well-rounded exercise routine, along with proper nutrition, can provide transformative results and empower women on their fitness journey.
Key Takeaways and Advice for Successful Gym Training
- Set realistic goals and track progress to stay motivated.
- Choose the right gym and seek guidance from qualified trainers.
- Prioritize safety by consulting healthcare providers and using proper equipment.
- Incorporate full-body workout routines that include warm-up, strength training, HIIT, and cool-down.
- Explore targeted workout routines to build strength and muscle.
- Include cardiovascular exercises like running, cycling, or swimming for overall fitness.
- Prioritize proper nutrition, balanced macronutrients, and hydration for optimal results.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- Can gym workouts make females bulk up?
Contrary to popular belief, gym workouts do not typically make females bulk up. Women have lower testosterone levels compared to men, making it challenging to develop significant muscle mass naturally. Instead, strength training helps women achieve a toned and sculpted physique while reaping the many health benefits associated with resistance training.
- How many times per week should a beginner female go to the gym?
The frequency of gym workouts will depend on individual goals, fitness level, and other commitments. Generally, beginners can start with two to three days of gym workouts per week, gradually increasing the frequency as they build stamina and strength. Listening to the body and allowing for adequate rest and recovery is crucial.
- Is it necessary to hire a personal trainer for gym workouts?
While it is not necessary to hire a personal trainer, working with a qualified trainer can provide valuable guidance, support, and accountability. A trainer can create a personalized workout plan, teach proper form and technique, and provide motivation throughout the fitness journey. However, beginners can also educate themselves through reliable resources and start with basic workouts.
- Are supplements necessary for achieving fitness goals?
Supplements are not necessary for achieving fitness goals. A well-balanced diet that includes a variety of whole foods can provide all the necessary nutrients for a healthy and active lifestyle. However, in some cases, individuals may benefit from certain supplements, such as protein powder, if their dietary intake is inadequate or specific deficiencies are identified through medical consultation.
- Can I see results without lifting heavy weights?
Yes, lifting heavy



